CORE Physical Therapy In Omaha Explains…
By Dr. Mark Rathjen PT DPT CSCS
CORE Physical Therapy Co-owner
17660 Wright St. 9/10
Omaha NE
402-933-4027
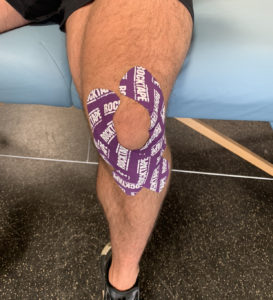
“Femoral rotational taping could alter patellofemoral kinematics and decrease pain in treatment of young female participants with PFPS.”
Taping can be a very effective tool to increase proprioception and muscle activation in our athletes. In Omaha, We have been performing KT and Rock tape applications for more than 20 years. When used appropriately, taping can lessen pain and help to increased recruitment. of muscles that are lacking in functional positions. Taping alone rarely solves all problems. IN combination with other modalities and Physical therapy regulated treatment programs can more quickly get an athlete back to full competition.
At CORE Physical therapy in Omaha, we have been utilizing KT tape and rock taping techniques since its inception. We strive to continuation of research of our Omaha athletes.
17660 Wright St, Suites 9/10
Omaha, NE 68130
402-930-4027
At CORE Physical Therapy in Omaha, We specialize in the treatment of athletes. We have worked with athletes for a combined 30 years. CORE was established in 2015 by Dr. Mark and Dr. Claire Rathjen is family owned and operated.
Proud winners of the Omaha Choice awards for 2016, 2017, 2018, 2019, 2020,2021
We are proud to serve the greater Omaha metro area.
For More information, Please feel free to contact us http://coreomaha.com/contact/
Please feel free to follow us at https://www.facebook.com/COREomaha/
To get started http://coreomaha.com/getting-started/
For more Blog information http://coreomaha.com/blog/
Youtube Account linked below.
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCVg8OSN5h-i1n_ykw1Gvahg?view_as=subscriber
Effects of femoral rotational taping on pain, lower extremity kinematics, and muscle activation in female patients with patellofemoral pain
- PMID: 25127530
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsams.2014.07.009
Abstract
Objectives: To explore the hip and knee joint kinematics as well as muscle activation between participants with patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS) and controls, and to investigate the immediate effect of proximal femoral rotational taping on pain, joint kinematics, and muscle activation during single-leg squat (SLS).
Design: Cross-sectional study.
Methods: Sixteen female participants with PFPS, and eight healthy female controls participated. Three-dimensional hip and patellar kinematics measured by electromagnetic tracking system, hip (gluteus maximus and gluteus medius) and thigh (rectus femoris) muscle activation measured by EMG, and subjective report of pain were recorded during SLS in three randomized conditions of no tape, sham taping, and femoral rotational taping with kinesiotape.
Results: Without taping, compared with controls, PFPS group had increased hip adduction angle (23.5±11.3° vs. 15.8±7.3°) during SLS. Additionally, PFPS group exhibited lesser rectus femoris activity during the initial 0-15° of SLS. Application of both femoral rotational and sham tapes reduced pain for PFPS group. Compared with no tape or sham tape, femoral rotational tape significantly shifted the patella into more posterior (1.59±0.83cm in no tape vs. 1.54±0.87cm in sham tape vs. 1.32±0.72cm in femoral rotational tape) and distal (-2.49±0.95cm vs. -2.64±0.80cm vs. -3.11±0.77cm) positions in the PFPS group.
Conclusions: Femoral rotational taping could alter patellofemoral kinematics and decrease pain in treatment of young female participants with PFPS.
Keywords: Anterior knee pain; Hip; Medial collapse; Patella; Single-leg squat.
Copyright © 2014 Sports Medicine Australia. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Similar articles
-
J Athl Train. 2008 Jan-Mar;43(1):21-8. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-43.1.21.PMID: 18335009 Free PMC article.
-
Clin J Sport Med. 2017 Sep;27(5):438-443. doi: 10.1097/JSM.0000000000000392.PMID: 28036322
-
